What about Miriade.psv
Miriade.psv is a service of the LTE Virtual Observatory project allowing the
computation and visualization of the apparent aspect (physical ephemerides) of the solar system objects: planets,
major satellites, asteroids and comets.
The service can be used as a Web service and easily integrated into your own software (cf.
Miriade.psv main page). We propose some examples of
client programs for that. The service can also be used through
a Web form which allows to define your input parameters, and to submit
requests. This page describes how to do with some of the input parameters of the service.
The positional ephemerides are computed by Miriade.ephemcc,
and the dynamical properties of solar system objects are the same.
The physical ephemerides are computed by Miriade.ephemph,
and the physical properties of solar system objects are the same.
The Miriade.psv service computes and draws the apparent aspect of solar system objects
from the output results of the physical ephemerides computed by ephemph.
See the Miriade.ephemph HOWTO for information
about the designation of bodies, epoch formats, observer's coordinates, magnitude filters, and thermal
flux computation.
How to use Miriade.psv service?
Several methods can be helpful:
- use the query forms made available on the LTE Solar system portal.
- implement yourself the Miriade Web service
psv method
into your own software (see client templates) or call the HTTP request
on the command line interface using non-interactive file transfert programs such as wget or curl (see the
how to consume section).
- use the Miriade services through a VO-compliant software which implements them, such as
Aladin and the Miriade
plugin, or other VO applications. For example
you can directly submit a request to Miriade.
psv in the Location entry of the
File → Load Table menu of Topcat software.
How to choose the physical model?
Physical models of solar system objects are listed by id, an integer value greater or equal to one.
Use the argument so=id to compute ephemerides with the corresponding physical model.
The list of available physical models can be retrieved by using the
HTTP request specific interface of Miriade.ephemph
service. Within the collected data, the id of the physical model is given by the value of the
ssomodelid parameter.
For most objects, id = 1 will allow to compute ephemerides with the recommended physical model.
For giant planets, id equal 1 to 3 corresponds to the classical systems I, II or III.
How to define the output format of images?
PSV can generate two kind of views:
wired: simple wired model, in PNG or POSTSCRIPTpsv: realistic model, in FITS or PNG
The general syntaxe for setting the view format of the output images is:
[wired:]png|eps | psv[:fits|png] | none
By default, the wired model is used, and images are in PNG.
For PSV views, the FITS format is set up by default.
It is possible to desactivate the image generator by using view=none. In that case
you should prefer to use the Miriade.ephemph
method, dedicated to the computation of physical ephemerides.
Examples: wired -> PNG EPS ; psv -> FITS PNG
How to set up PSV options?
The psvopts argument allows to pass options to the image generator, in order to
control some parts of the drawing.
Wired model
The general syntaxe is a list of options separated by the semicolon character:
psvopts="zoom=a[,b];label=0|1;showorbit=0|1"
where:
zoom=a[,b]- Defines the bounds of the x and y axes with the value ±a, and ±b for the y-axis
if provided. Examples:
zoom(2) plot a scene of ±2 Sso radius along x and y axes;
zoom(9.0,1.7) plot a scene of ±9 Sso radius in x, and ±1.7 Sso radius in y.
label=0|1- Displays (default) or not (0) the labels in the image.
showorbit=0|1- Materialize the orbit of all the components of the asteroidal system. Default: 0.
Example:
psvopts="showorbit=1",
psvopts="zoom=2;showorbit=1"

PSV model
The general syntaxe is a list of options separated by the semicolon character:
...
where:
resolution- Dimensions (intarr(2) of the output images in X and Y. Default is TBD.
fov- Dimension and orientation of the Field of View (FoV). IDL structure where fields are:
.X: Size of the FoV along x axis.Y: Size of the FoV along y axis.UNIT: Unit for the size of the FoV (deg|min|sec).PA: Rotation of the FoV (from North to Y, direct sense, degrees)
showStar- Boolean to display (1) or not (0) the stars within the FOV. Default is 0.
showSSO- Boolean to display (1) or not (0) the Solar System Objects within the FOV. Default is 0.
magLim- Maximum magnitude (float) to display stars and SSOs. Default=10.
\par Examples: config='CHeMIN',
psf={ display: 0/1, type: 'seeing'/'diffraction'/'user',
size: 1.0, [arcsec]
wavelength: 1.0, [micron]
aperture: 1.0, [m]
path: 'CHEMIN vers psf user' }
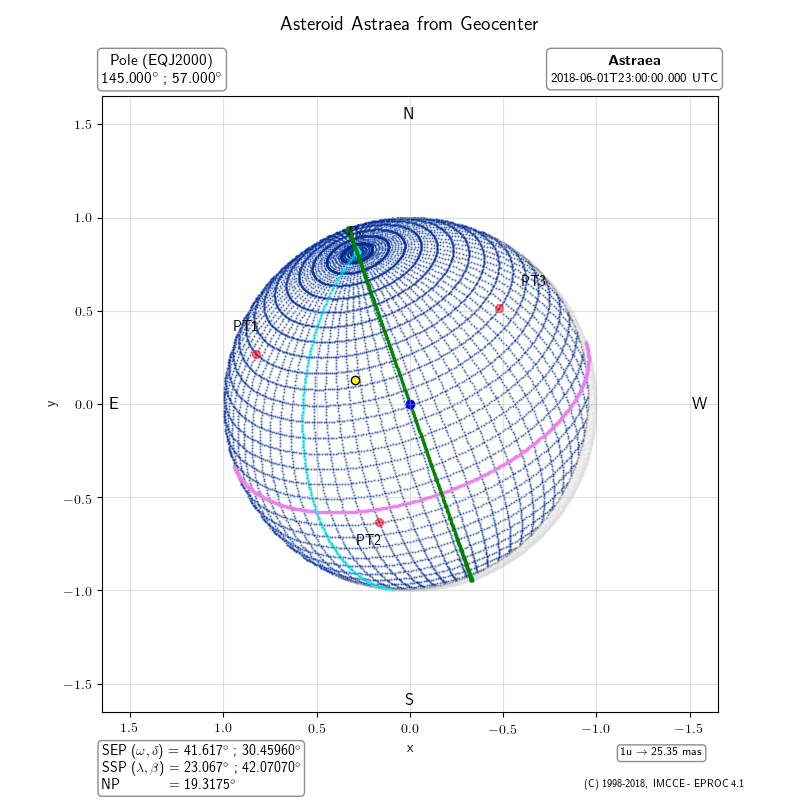
How to define features?
To plot marks on the surface of the body to indicate features, define a list of equatorial
planetocentric coordinates of the features, serarated by the semicolon character:
features="Label,longitude,latitude[;Label,longitude,latitude]"
Each feature, visible from the observer, is displayed as a circular red mark with the given label.
Example: features="PT1,35.0,45.0;PT2,340,-5.0;PT3,264.0,40.0"